Best Practices
Explanations with Examples of Well-Constructed Questions
Here, you will be presented with questions that can be considered successful. An analysis will illustrate why each question is a good one.
3 Types of Relevance of the Question
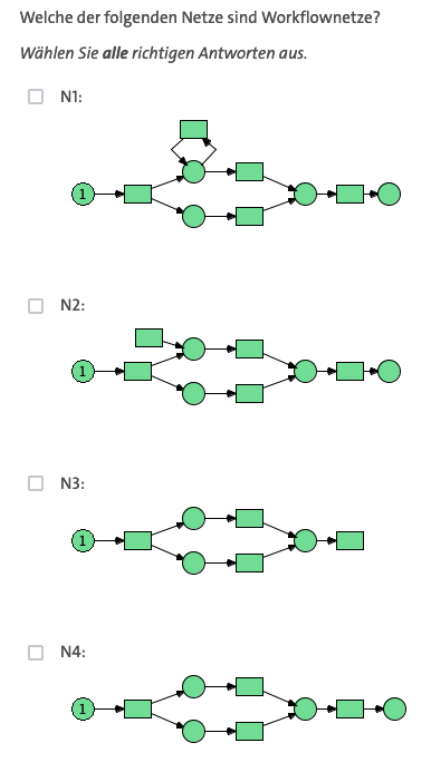
- Understandable sentences and emphasis ("all")
- Clearly recognizable division of the question
- Knowledge transfer (knowledge of the definition of workflow networks is required to apply this)
Relevance of the question:
- By subject area (workflow networks are an important subclass of Petri nets)
- Sustainable (foundation for modeling in computer science and other subjects)
- N1 indicates the misconception that cyclical behavior in workflow networks is not possible
Higher Learning Objectives and Significant Consequences of Errors
An online retailer offering goods to consumers creates a YouTube channel and uses the following legal notice (Impressum).
Examine whether this constitutes an error-free legal notice. Take into account any changes in current legal jurisdiction. Justify your answer.
Provider Identification
Provider and responsible for these pages as well as the appearances of kaufdirwas.de is
Kauf dir Was GmbH
Hohenzollernring 6
50677 Cologne
Tel: +49 (0) 221 – 3587 334
Fax: +49 (0) 221 – 3587 332
Email: service@kaufdirwas.de
The VAT identification number is: DE 206273408.
represented by:
Markus Müller (Chairman)
Dr. Peter Gerstmann
Anna Boniface
Solution pattern: The Impressum is faulty because, as an online retailer for consumers, it lacks the notice about the dispute resolution platform and the information on possible participation in it.
- Relevance of the question: Errors can have significant consequences → Legal warnings (Abmahnungen) may occur
- Higher learning objectives: Analysis
Plausibility and Homogeneity of Distractors
A good multiple-choice question is also characterized by how plausible the distractors are. In the section "Construction of Multiple-Choice Questions," we asked about the capital city of Rhineland-Palatinate. All the cities listed belong to Rhineland-Palatinate. If the radius had been expanded to include neighboring cities from other states, such as Mannheim, the question would have been somewhat easier to answer. Including well-known cities from across Germany could have eliminated further distractors.
Example: Which artist is known for the fresco "The School of Athens"?
a) Botticelli
b) Michelangelo
c) Raphael
d) Perugino
e) Da Vinci
Regarding the plausibility and homogeneity of the answer options, this is a good question. All the alternative answers are plausible and homogeneous (Italian painters who worked during similar times, and could potentially be responsible for the fresco). No solution hints can be derived (except that the answer is c) and is in the middle, which should not happen too often in other questions).
Clarity: Each answer option could also be written out in a sentence. However, this would test reading comprehension, which is not the intended focus, creating an unnecessary hurdle. Additionally, the first format provides time advantages for both instructors and students.
Question Distribution and Transfer Performance
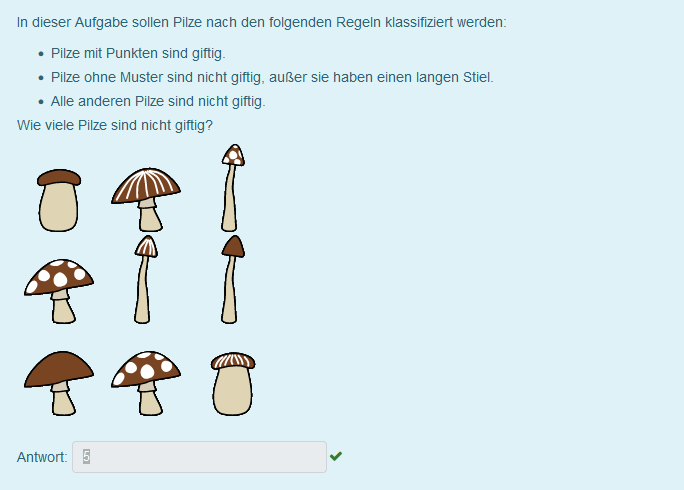
- Clear and recognizable division of the question (naming the action required to solve the question; listing rules as a list; main task).
- Comprehensible sentences and illustrations (recognizability of patterns and length specifications).
- Use of an illustration as an advantage of electronic examination.
- The question does not ask for pure knowledge. Instead, knowledge learned through the task should be applied. A transfer of the newly learned content takes place.
Criticism: the guideline 'use of negations' (not toxic) and their emphasis (bold, italic) is not adhered to.
Scope of application: primarily for formative assessments due to low difficulty level or practice exams to familiarize students with learning software and question types.
Relevance: Confusions as Common Errors

- Relevance of the question: frequent confusion between empty language (∅) and empty word (ε)
- Clear and recognizable division of the question (assumption, question, action instruction)
- Comprehensible sentences and emphasis ('all')
- Knowledge transfer
